Options Trading Comprehensive Guide – Secrets of Calls and Puts


Overview
You know, options trading is extremely lucrative and a bit like a rollercoaster ride in the stock market! Some say it’s a real ‘Hera-Pheri‘ because you can win big, but you can also lose big. It’s like taking shortcuts in life – exciting but very risky!
In options, folks bet on whether prices will go up or down. Sometimes, you’ll feel like you hit the jackpot, just like ‘Dene Wala Jab Bhi Deta, Deta Chappar Phaar Ke.’ But if you’re not armed with technical knowledge, mostly, you’ll find yourself under a pile of debts like ‘Baburav’ with ‘Udhar Walas’ at your door. And if you’re here to gamble based on news and tips, get ready for more ‘Mere Ko To Aisa Dhak Dhak Ho Rela Hai‘ moments!
The stock market is highly dynamic, so is our theory of demand and supply. But first, let’s dive into the action and start with the basics of options trading, made super simple for you.
What Are Options?
Imagine options trading like a special contract. This contract gives you a unique right to buy or sell a certain number of securities or other assets, at a fixed price in future. With these special rights, you also get the choice to use these special rights if you want to but not obliged (forced) to do so. But you can do this either before a specific date or on that date itself.
In technical terms, options are part of a larger family of financial tools known as “Derivatives.” Think of them as the cool cousins of the finance world. The price of a derivative set on the base of price of some other asset, such as forward and futures, puts, calls, swaps, and mortgage-backed securities. These cousins are all about adding excitement and creativity to your investments, making your financial journey a lot more interesting and rewarding.
Interesting Fact: Options trading wasn’t initially exercised into The Wall Street. It was agricultural trader and indigenous farmer, William Garratt who practiced options trading in 1848 after analyzing the market risk.
Now, you might be thinking, “Why should anyone be interested in options?”. Well! As said in the beginning, options can add an exciting depth to your financial journey – huge depth if done right.
Picture this: You’re looking for ways to hike your incomes and options can be your side hustle. It can help you with extra funds and make your life a little more colorful and convenient.
Options can also be your financial safety net. They work a bit like an insurance policy for your investments, helping you avoid significant losses. It can also be your financial superpower and provide a way to increase your investments, making them more powerful. It’s a bit like getting more bang for your buck in the world of finance.
Key Takeaways:
- Options are like special tools for making financial bets.
- Call options are like “I want to buy” bets, while put options are like “I want to sell” bets.
- Call options allow you to buy something at a set price before a specific date.
- Put options let you sell something at a set price before a particular date.
- People use options for various reasons, from making predictions to protecting their investments.
Disclaimer: Options involves significant market risks and may not be suitable for everyone. It includes forecasting and a significant risk of financial loss.
What is Strike Price
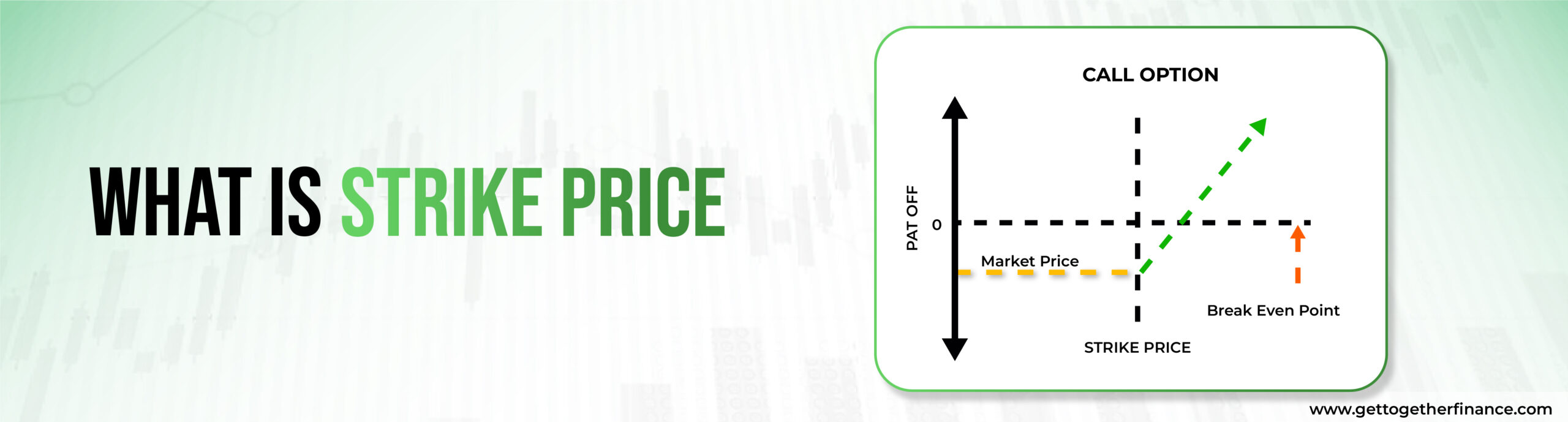
The strike price, also known as the exercise price, is like a pre-decided tag or “agreed-upon” price on an option. It’s the price set in advance for buying or selling the underlying asset. This price is fixed when you create the options contract and plays a big role in deciding how profitable your options trade can be. It’s a bit like the price tag on an item in a store, telling you what it’s worth in the market.
Also Read: Stock Options Made Simple
How Options Trading Work?
Options trading works like the agreement that allows you to pick whether you want to buy or sell an underlying asset, such as stocks, at a certain price (strike price) on a specific date work (the expiration date). Imagine this – you make a reservation at a restaurant: you select what to order, at what price, and when you want to enjoy your meal. Options can be a way to manage risks.
Let’s take an example for better understanding. Options are a bit like making a deal, Indian style. Imagine you’re at a street market, and you spot a beautiful silk scarf. You can reserve it for a fixed price, say ₹500, and you have the choice to buy it within a week. Now, let’s break it down:
- Reservation: You’ve essentially made a reservation for that scarf. You don’t have to buy it if you change your mind.
- Fixed Price: ₹500 is your “strike price.” It’s the price you’ll pay, no matter what the market price of the scarf is when you decide to buy.
- Time Frame: You’ve got a week to decide – it’s like a limited-time offer.
Now, how can this be handy? Let’s say the market price for that silk scarf suddenly shoots up to ₹800 during the week. You can still buy it for ₹500 – that’s your right! But if the market price stays the same or drops, you’re not obliged to buy it; you just let your reservation expire.
You can make a deal to buy or sell an asset at a set price within a certain timeframe. It’s a tool to manage risk, speculate on price changes, or even create income, just like haggling at a bustling Indian bazaar!
Types of Options: Call and Put

Like the spices in an Indian kitchen, options also come in different flavors, each with its unique purpose and taste. There are two types of options trading you can go with– call and put. Let’s uncover the sheets and dig deeper into these concepts to make the concept clearer:
Call Options
Picture this: You bought a train ticket to reserve a seat in the train at a predetermined price and time. Now, no matter if the fare of the train ticket goes up or down, you have the seat booked for you. You are free to choose whether you want to use the services or not. That’s a call option. Even if the price of the asset goes up, you can still purchase the security at the agreed-upon rate within a specific timeframe.
Quick Fact: Only about 10% of contracts actually get used when they expire. And here’s the twist – it doesn’t mean rest were useless while they were in play as trader could use it whenever they want before the expiry date.
Call options gives you the right to “call” or buy an asset at a set price within a specific time period. There are two types of call options popular in the stock market:
- American-Style Options: These are like versatile options that let you buy the asset anytime until the expiration date. It’s a bit like having the flexibility to buy your favorite snacks whenever you want.
- European-Style Options: These options are a bit more specific. They only allow you to buy the asset on the actual expiration date, like celebrating a birthday on the exact day. You can’t do it earlier or later.
These two options styles offer different ways to plan your investments, like choosing between two different kinds of adventures, each with its own rules and rewards.
Call Options Example
Let’s take a simple example in the Indian stock market. Imagine you are interested in, “ABC Ltd.,” and you think its stock price will shoot up in soon. Now let’s explore how a call options work:
- Selecting a Company: You pick “ABC Ltd.” as the company you’re looking at.
- Strike Price: Currently, “ABC Ltd.” stock is priced at ₹1,000 per share. You chose to get a ‘call option’ with the same strike price and want to buy the stock.
- Premium Payment: Now you pay the premium token price of this stock of, let’s say, ₹50.
- Expiration Date: And you select an expiration date, maybe one month from today.
Here is how it plays out:
If the stock price of “ABC Ltd.” go up than ₹1,100 per share by the expiry date, you can choose to use your call options, buy the stock at the lower strike price or potentially sell it at the higher market price, making your personal margin.
However, if the stock price remains below ₹1,100, or doesn’t flick much, you can choose to not use your option and let it expire. This will only cost you premium token amount you’ve paid, i.e., ₹50.
So, now you see, call options offer you a smart way to profit from rising stock prices without paying the complete price for a stock. It’s like reserving the right to buy something at a lower price, but with the flexibility to change your mind if things don’t go as planned.
Put Options
On the flip side, a put options is akin to reserving the right to sell your product or asset at a fixed price within a set period of time. Imagine this as securing the option to sell your old scooter for a fixed price. If the value of your old scooter drops, you will still be able to sell it at higher price.
Quick Fact: Mary and William in London started using puts and “calls” back in the 1690s as trading tools. It’s like they had a taste of trading options centuries ago!
Put options act like the shield of your investment from unexpected market falls or storms. You might not always require the shield, but when you do, it will be here to help you with the upcoming trouble. Both call and put options offer different strategies to lead your finance journey in the market, like selecting between sweet and savory snacks at a chai stall – all depends on the mood, weather, and situation. But first, let’s understand the concept better with an example.
Put Options Example
Let’s start with a simple example. Imagine you already own 100 shares of “XYZ Company,” each worth ₹1,200, and you feel like market is going to take a dip. Now, let’s calculate how this is helpful for you:
- Stock Ownership: You’ve got 100 shares of “XYZ Company” in your portfolio, each share of ₹1,200.
- Enter the Put Option: Now you decide to buy a put options with a strike price of ₹1,100, and it lasts for one month. The cost? Just ₹50.
- Market Dips: Unfortunately, the market takes a down spin, and the share price drops to ₹1,000 each.
In this case, let’s see how the put options comes to your rescue:
You get the rights to sell your 100 shares at the agreed-upon price (₹1,100), even though the market rate is just ₹1,000, thanks to put option. This means your probable loss per share is limited at ₹100. It offered you a shield against the market’s mood swings.
In simple terms, the put options acts like financial insurance, safeguarding your investments when the market doesn’t play nice. It’s your backup plan for those unpredictable moments in the stock market.
Difference Between Call v/s Put
| Aspect | Call Options | Put Options |
| What it offers | The right to buy an underlying asset at a strike price | The right to sell an underlying asset at a strike price |
| Profit in Bull Market | Potential for profit when the market price rises | Limited profit when the market price rises |
| Profit in Bear Market | Limited profit when the market price falls | Potential for profit when the market price falls |
| Obligation | No obligation to buy the asset (only a right) | No obligation to sell the asset (only a right) |
| Risk | Limited to the premium paid | Limited to the premium paid |
| Strategy | Used for bullish strategies and speculation | Used for bearish strategies and protection |
| Example | Buying call options on a stock you expect to rise | Buying put options on a stock you expect to fall |
What is Option Buying and Option Selling?
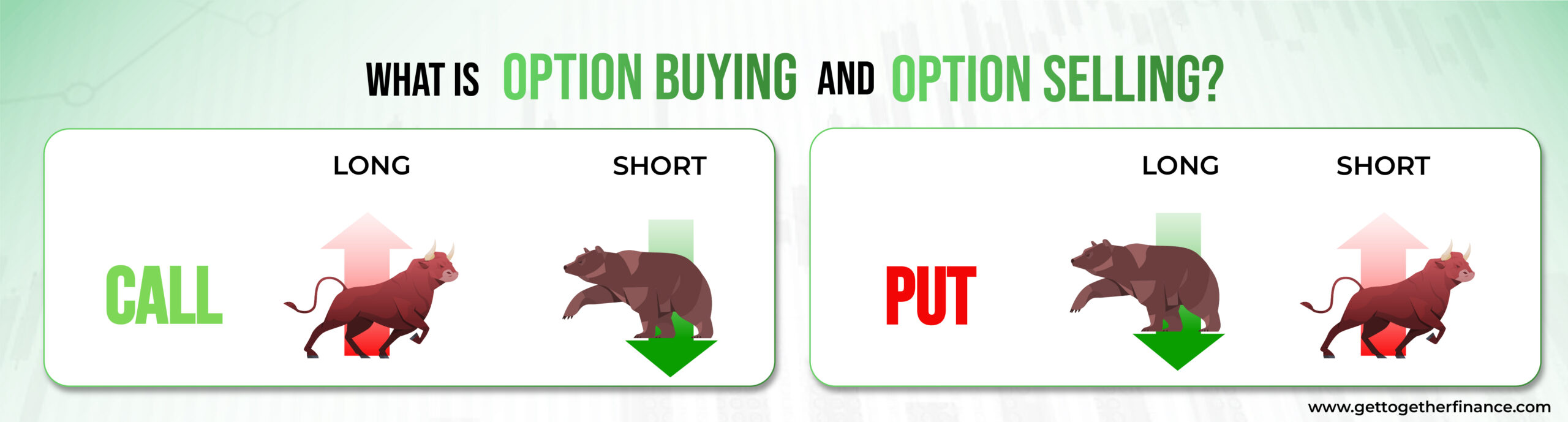
In brief, options are the derivatives that offer you right to buy or sell a security at a selected price at fixed data in the future. It’s a bit like game between two key players – options buyers and options writer, also known as the options seller.
Options Buyer (Player 1)
Imagine the options buyer as someone with choices to make, a bit like deciding which movie to watch. You can select a security and choose to make a purchase in specific time and rate in the future. An options buyer has the choice to select the game they want to play at the game zone.
The important thing is to remember that an options buyer doesn’t have any obligation to do anything if they don’t want to. It’s like buying a movie ticket to book the seat at movie hall, however, you have choices either to go or to not go for the movies. Although, you have spent the money on it.
Fact Check: Did you know that a majority of options bought by individuals are never exercised? That’s right, around 70-80% of options bought simply expire without being used. It’s a reminder that having choices in the financial game doesn’t always mean you have to act on them.
Options Writer (Options Seller – Player 2)
On the contrary, options writer, also known as options seller are the ones who offer a service or delivery stocks. Just like a service provider, a bit like your favorite pizza place delivering your order. Now imagine, this service provider has given you a ticket (commitment) to a movie, and when you appear to movie hall, they are ready to do what they have agreed to. Options writer (seller) are obligated to deliver you the service they have committed to as per the terms of options agreement.
When it comes to options trading, both options buyer and options seller (options writer) acts differently in different types of options. Let learn more about it in more details:
What is Call Options Buyer and Call Options Writer (Call Options Seller)?
Call Options Buyer
Call buyers are like optimistic folks, bullish in nature. They expect prices to go up, and they’re excited about it.
- Call buyer is someone who buys a call options, expecting the price of asset will go up.
- By buying a call options, they get the right to purchase the asset at a set price.
- They pay a premium for this right and can choose to use the option or let it expire.
The best part? If prices go way up, buyers can make a lot of (unlimited) money. But their worst-case scenario is just losing the premium they paid (limited loss). So, they have potential for big wins with limited risk.
Call Options Seller (Options Writer)
Call sellers are a bit more cautious. They’re not so sure prices will go up. They act not bullish (sideways, bearish).
- Call seller is usually someone who owns the asset.
- By selling a call options, they agree to sell the asset if the buyer exercises the options trading.
- They receive a premium to get the right to sell and are obligated to sell.
- They profit if the option isn’t used. The profit is limited but the loss is unlimited.
The catch? If prices skyrocket, the call seller’s losses can keep piling up. But their profit is limited to the premium they received. So, they’re not in it for big gains; they prefer staying safe.
Note: When a call options buyer enters the picture, they get the choice whether to purchase the stock or not (not obliged), but will still pay the premium regardless the order execution. On the flip side, option seller obliged to sell the stock at the fixed price upon the request of buyer.
What is Put Options Buyer and Put Options Writer (Put Options Seller)?
What is Put Options Buyer?
Put buyers are like realists. They think prices will fall, and they’re prepared for it. Put buyer acts bearish.
- Put buyer purchases a put options and expect the asset price to go down.
- By buying put options, they get the right to sell the asset at a set price.
- They pay a premium for the right to sell and are not obliged for it.
Here’s the cool part: If prices really drop, they can make a nice profit. But if things don’t go as expected, their loss is limited to the premium. So, they’re ready for the worst while hoping for the best.
What is Put Options Seller (Option Writer)?
Put sellers are open-minded. They don’t mind which way prices go – up, down, or sideways. Put options seller acts not bearish (bullish, sideways).
- Put seller is usually someone who doesn’t own the asset and ready to sell put options.
- By selling them, they agree to buy the asset if the buyer exercises the options trading.
- They receive a premium for taking on this obligation.
- They profit is limited yet loss is unlimited.
In simple terms, call buyers bet on prices going up, call sellers are ready to sell if prices rise, put buyers bet on prices going down, and put sellers are ready to buy if prices fall.
| Aspect | Call Options Buyer | Call Options Seller | Put Options Buyer | Put Options Seller |
| Market Outlook | Bullish (Positive) | Neutral | Bearish (Negative) | Neutral |
| Right/Obligation | Right to Buy | Obligation to Sell | Right to Sell | Obligation to Buy |
| Premium Payment | Yes | Receives Premium | Yes | Receives Premium |
| Profit Potential | Unlimited | Limited to Premium | Unlimited | Limited to Premium |
| Loss Potential | Limited to Premium | Unlimited | Limited to Premium | Unlimited |
Uses of Call and Put Options
You know, call options and put options have their uses in different situations. Take a look at the table below to see when and why people use them.
Call Options
- Buying Call option buyers use them to protect themselves if they think the price of something might go down. It’s like an insurance policy for your investments.
- American importers use call options on the U.S. dollar to safeguard their buying power in case the dollar loses value.
- People who own stocks in foreign companies use call options on the U.S. dollar to protect their dividend payments.
- Short sellers (those betting on stock prices going down) use call options to hedge their bets.
Put Options
- Buying Put option buyers use them as a safety net if they believe the price of something could go up. It’s like locking in a good deal in advance.
- American exporters use put options on the U.S. dollar to secure their selling costs in case the dollar’s value rises.
- Manufacturers in foreign countries use put options on the U.S. dollar to safeguard against a drop in their own currency when they get paid.
- Short sellers don’t benefit much from put options because a stock’s price can’t go below zero.
In simple terms, call options are like insurance against falling prices, while put options are safeguards against rising prices. People in various financial situations use them to protect their interests.
How to Trade Options

Trading options is like making deals in the stock market playground. To start the trading, you’ll need a demat account with a broker who offers a platform for options trading. Once you’re done with the initial set-up, you can start your finance journey.
Here is how trading options work:
Choose Your Game: Options come in two flavors – calls and puts. If you feel like “I think the price of this thing is going up,” you can pick call. But if your study says that, “I think the price is going down” you can pick put. What you need to do is pick your strategy.
Pick Your Player: Later, you need to pick an asset or stock you want to play with like picking the team members for your game.
Set Your Rules: The most important part of options trading is to decide when you want to make your move. Like a game clock, every option has an expiry date and a set strike price. It’s up to you whether you want to go for a short time or a long play.
Place The Bet – Entry: Place the bet on either buy or sell options. Buy call option if you feel that price will go up and buy put option if you feel like price will go down. Just like in a game of cards, you’ll have to decide if you’re holding onto a winning hand or folding.
Game On – Add Exit and Stop-Loss: Well, now that you have made your moves, game on! Keep a close look on the market, add your exit points and stop-loss to minimize the market risks.
Remember, like every other game, options trading also involves risks. Best players practice hard and believe in learning from experience. So, this is important to understand the strategies and rules of the game before you start playing. This will help minimize the chances of loose.
Why Trade Options?
Trading options is an appealing choice for investors as it brings a huge profit on the table. Imagine this, a person offers you 10 candies in 5 years for 50 RS. On the other side, you can make those 10 candies in 5 months. But here is the catch – the risk is considerably too high, and you might end up with nothing at all. Tough choice, right!
Options provide flexibility to profit from various market conditions, including bullish, bearish, or range-bound markets. It also offers leverage to multiply gains with a smaller upfront investment. Additionally, it can help generate income through strategies like covered calls. But, it’s crucial to note that options trading involves risks and complexities, needing a solid understanding of the market and strategies.
Note: It is important to educate themselves, develop a clear plan, and consider professional advice, before trading options. There is no guarantee of benefit or loss in the market.
Risks and Potential Benefits (Advantages and Disadvantages) of Options Trading

Stock market comes with risk and surely options trading is not friends with you, unless you know everything about it. It’s like a cat who will only purr if you know it thoroughly, including its likes and dislikes. Here we have mentioned few potential benefits and risks (cons) of options trading.
Advantages (Potential Benefits):
- Leverage: Options allow you to control a larger position with a relatively small amount of money. This can amplify your potential profits.
- Risk Management: Options can act as insurance for your investments. They provide strategies to limit losses and protect your portfolio.
- Income Generation: You can generate income by selling options. This can be especially appealing in flat or stable markets.
- Versatility: Options offer various strategies, allowing you to profit from different market conditions, whether it’s bullish, bearish, or neutral.
Disadvantages (Risks):
- Limited Time: Options have expiration dates. If the market doesn’t move in your favor within the given time, your option can expire worthless.
- Complexity: Options can be complex, and understanding the strategies and risks requires education and practice.
- Potential Losses: While leverage can amplify gains, it can also magnify losses. You could lose more than your initial investment.
- Market Volatility: Options are sensitive to market volatility. Rapid price swings can lead to unexpected outcomes.
- Fees and Commissions: Options trading often involves fees and commissions, which can eat into your profits.
If you want to take a brief look at all the potential benefits and risks, here we have simplified this for you:
| Advantages (Potential Benefits) | Disadvantages (Risks) |
| Leverage: Amplified potential profits | Limited Time: Options expire |
| Risk Management: Portfolio protection | Complexity: Requires education |
| Income Generation: Selling options | Potential Losses: Losses can exceed initial investment |
| Versatility: Profit in any market | Market Volatility: Sensitive to unexpected price swings |
| Fees and Commissions: Trading costs |
In essence, options trading offers opportunities for both gains and losses. It’s crucial to educate yourself, have a clear strategy, and manage risks effectively when venturing into this market.
American vs. European Options
In the stock market, you can explore both European and American options. Both of them share many similarities, but the differences between them are also very important. Here let’s learn about them in brief:
American Options:
These are like all-access passes. With American options, you can buy or sell your underlying assets any time you want, right up until the expiration date. It’s like having the freedom to make your move whenever it makes sense for you. This is the reason why American options carries higher value in the market comparatively.
European Options:
Think of these as more exclusive. European options only allow you to exercise your right on the expiration date itself. So, you don’t have the flexibility to make any exchange of asset before that day. It’s a bit like having a ticket to a show that only works on the show date; you can’t use it earlier.
There are more exotic options out there like knock-out, knock-in, barrier options, lookback options, Asian options, and Bermuda options. Exotic options are special because they’re not like regular options with unique ways of paying out, different expiration dates, and strike prices. However, you have to keep in mind that these are mainly used by professional derivatives traders.
In a nutshell, American options give you more control because you can choose when to act, while European options have a fixed exercise date. It’s like comparing an all-day buffet (American) to a reservation-only restaurant (European).
Options Trading Strategies You Must Know
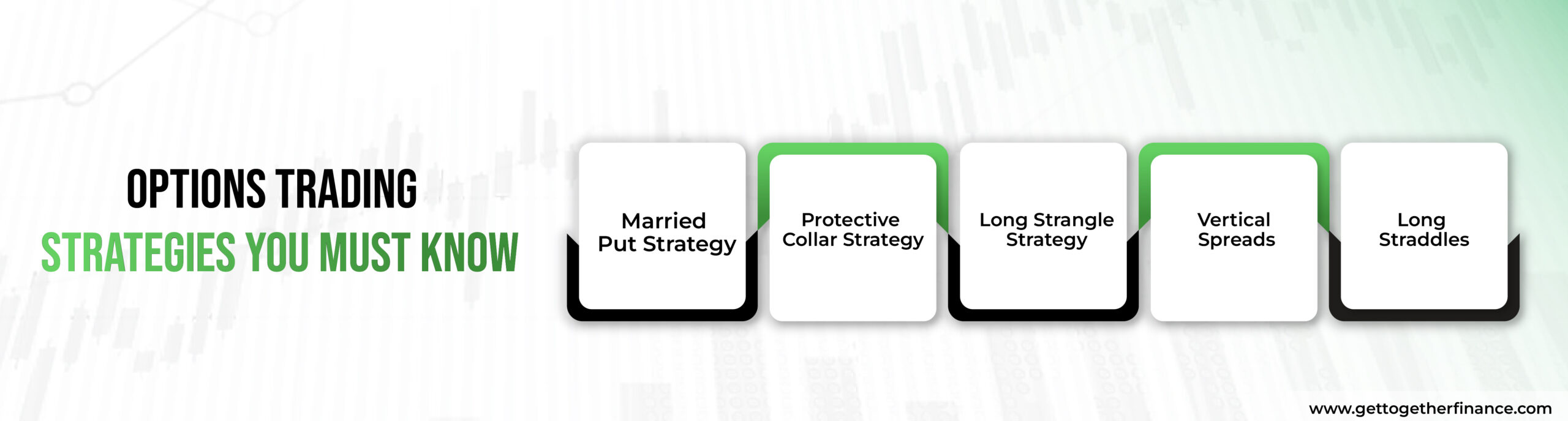
Amature traders jump into the options trading without having the proper knowledge of operation strategies. These are not just strategies; these are ways to limit your risk and maximize your return on benefit. Here are few strategies listed just for you.
Married Put Strategy
When you buy a stock and get insurance (a put option) for it. In case if the stock price falls, your put options lets you sell the stock at a fixed price to limit your losses.
Protective Collar Strategy
You own a stock and buy insurance (a put option) while also renting out a part of your stock (selling a call option). It’s like protecting your house with insurance while letting someone rent a room in it.
Long Strangle Strategy
You buy both – a bet for rise in the price (call option) of higher strike price and a bet for fall in the price (put option) of lower strike price at the same time. You’re hoping for a big move in the stock price, no matter which way it goes.
Vertical Spreads
You make two bets on a stock with different price levels. It’s like saying, “I think the stock will move, but not too much.”
Long Straddles
You place the bet for price rise and a bet for price drop at the same time. You’re saying, “I’m not sure which way it’ll go, but when it does, I want to be there to profit.” It is different from long strangle strategy because long strangle involves different strike prices, whereas long straddles include the same strike price.
There are few other strategies that are famous among traders, including Iron Condor, Long Call Butterfly, Bear Put Spread, Bull Call Spread, etc. Remember, each strategy has its own risks and rewards, so make sure you understand them before using them in your trading.
Is Trading Options Better Than Stocks?
Think of trading options and trading stocks like using different tools from a toolbox. The difference is owning a stock is like owning a piece of a company. You can wait for them to grow over time, but there’s a risk if the value of company goes down. Now, on the other side, options are more like agreement that let you control stocks without keeping too much money upfront at stake. They can be a bit tricky to follow and come with high risks. But options offer you ways to make money whether their price remain straight, or go up and down.
In brief, it’s all about your knowledge of work, what you want to do, and how comfortable you are with taking a bit of risk. Just like picking the right tool for the job – sometimes you grab a hammer (stocks), and sometimes you need a wrench (options).
How Can I Start Trading Options?
Getting started with options trading is easier than you might think. Many online brokers now offer options trading such as Dhan, Zerodha, etc. and the process is fairly straightforward. First, you’ll typically need to apply for options trading and await approval from your chosen broker. Next, open a margin account as often it is a requirement by service providers.
Once you’re approved, you can start placing orders to trade options, much like you would for stocks. Access the option chain just like a menu of accessible options contract. Select the expiration data, the underlying asset (e.g., Apple) and the strike price. You need to make a decision whether you want to select a call options or a put option.
Remember, options trading can be both exciting and complex, hence it’s important to start with a clear risk management strategy and right mindset while staying informed about market developments.
What Are the Charges for Options Trading?
In India, when you trade options, there are some charges you should be aware of. Similar to the theme park analogy, you’ll discover various fees.
- First, there’s a brokerage fee, which is like your entry ticket to the park.
- Then, for each option contract you trade, there’s a per-contract fee, like paying for individual rides.
- Additionally, there might be a Securities Transaction Tax (STT), which is like a tax you pay when you buy or sell options, and it’s collected by the government.
It’s essential to keep these charges in mind while trading options in India, just as you’d consider your expenses when planning a visit to a theme park. Different brokers may have different fee structures, so it’s wise to compare and find the most cost-effective option for your options trading adventure in India!
The Greeks of Options Trading

The question is – what are the Greeks of options trading? No, we’re not talking about ancient philosophers. These are rather Greek symbols assigned to find and label the market risk to help traders understand and manage their options positions.
Delta
Think of Delta as the speedometer of your option. It tells you how much the option’s price is likely to move in response to a RS 100 change in the underlying asset’s price. For example, if an options has a Delta of RS 70, it suggests that for every RS 100 increase in the stock price, the options price will rise by RS 70.
Gamma
Gamma is like Delta’s sidekick. It measures how fast Delta itself changes. In other words, it tells you how much the Delta might increase or decrease as the stock moves. This is crucial for managing risk in dynamic markets.
Theta
Theta is the clock ticking on your option’s time value. It represents the daily loss in the option’s price due to the passage of time. As an options holder, Theta reminds you that time is money, and the longer you wait, the more value your options loses.
Vega
Vega measures an option’s sensitivity to changes in implied volatility. In simple terms, it tells you how much an option’s price is likely to benefit or loss for every 1% change in implied volatility. Traders use Vega to assess how market volatility might affect their positions.
Rho
Rho is the least talked-about Greek, but it’s still important. It measures how much an option’s price is likely to change for a 1% change in interest rates. Typically, Rho is more significant for longer-term options.
Understanding these Greeks is like having a navigation system for your options trades. They help you assess and adjust your risk exposure, providing valuable insights into how your options might behave in different market conditions. So, as you venture into the world of options trading, keep these Greeks in mind – they might just become your trusted allies in the markets.
What Do Critic Say?
Critics of options trading puts a unique viewpoint in this matter. Comparing it with catching a tricky butterfly with your hands – options trading is not easy and most people get lost and loose it all, believing on the news and reports. According to the data, 70% – 80% of options expire without being used. This is one of the reasons why you should know it all from inside out before jumping into the ocean options trading.
Another point that our expert traders and instructor emphasize on every class is not believe on market news, reports, or any sort of insider tip. Market is risky and believing untrusted information increases the risk. It’s important to know the beats of the songs to synchronize with dynamic market on every rhythm.
Ramesh Sharma, expert trader quoted, “It’s important to learn to drive a car before focusing on how to control it first.” Professional focuses on learning the dance of options trading – it may take time, but once you master your dance steps, you can wiggle your way to success.
In A Nutshell
Options trading is your short-cut to heaven or hell – the choice is yours to make! As critics raise valid concerns, if you approach towards it with well-thought-out plan and the right guidance, you can be master of your destiny. On the other side, the data of people who lost it all is higher than the ones who gained. You can either pick one of best course of learning technical analysis, or you go with the one of the most reliable GTF Options course and start a safe yet consistent journey toward your generational wealth.
FAQs
What is long call, short call, long put, and short put?
Nowadays, many brokers let qualified customers trade options. There are several strategies you can use to slay the game of options trading including long call, long put, short call, and short put. Here, let’s explore it in brief:
Long Call: Imagine you visit a luxury car store with the intention of buying a red car, but the only car available is white. The owner informs you that there will be a red car available next week, but the price may change. In response, you strike a deal with the store owner by paying a premium upfront. This means that even if the price goes up in the future, you will still pay the agreed fixed amount. This is essentially what a long call options is like. Long call options are bullish because they grant holders the right to purchase stocks at a predetermined price, and the premium paid secures this privilege.
Short Call: To understand it better, let’s take an example. Suppose you’re at a luxury car store, and you’re planning to sell the same red car next week. But you’ve got this sneaky feeling that the price might drop next week. What do you do? You make it deal with the owner, regardless how the price drop. This is what we call a short call option. Short call obligates you to sell the stock and offer you margin in exchange. Sweet, isn’t it?
Long Put: This time, let’s assume that you don’t own the car, but you think the price will drop. But what you have in mind is to make some profit from it. Now, you pay a small premium and someone makes an agreement with you that they will buy the car in specific price in the future, even if the price drops. That’s a long put. In this, you bet that the price will drop and you’re paying for the right to sell at a higher price. Simple, isn’t it
Short Put: In this, imagine you’re the car dealership owner. You already own some car and assume that market price will go up. You make an agreement with some who doesn’t own any car to buy their car at a pre-determined price in the future. Well, the deal is, you’re betting that the price of stock will either rise or stay same, and you get the profit for making that promise.
Remember, these options can be about things other than cars – like stocks or other assets. And just like in any bet, there are risks involved, so it’s important to understand how they work before using them in the real world.
When Do Options Trade During the Day?
Options typically trade during regular market hours, which in India are from 9:15 AM to 3:30 PM, Monday through Friday. These are the same hours when stocks on Indian exchanges like NSE and BSE are traded. However, there can be extended trading hours for certain options contracts, but those vary depending on the exchange and the specific contract. It’s essential to check with your broker or the exchange for the exact trading hours of the options you’re interested in.
Can You Trade Options for Free?
Trading options usually isn’t entirely free, as there are costs associated with options trading. These costs include:
Brokerage Commissions: When you buy or sell options contracts, your broker typically charges a commission for facilitating the trade. The commission can vary depending on the broker and the number of contracts traded.
Contract Fees: Some brokers may charge additional fees per options contract traded. There can be add-on fees, especially if you trade a large number of contracts.
Bid-Ask Spread: Options include bid and ask prices, and its difference is known as the bid-ask spread. When you trade options, you may incur costs associated with this spread.
Exercise and Assignment Fees: If you choose to exercise your options or if your options get assigned, there may be fees associated with these actions.
Regulatory Fees: Regulatory authorities may charge fees on options trades, which are usually passed on to traders by brokers.
While there are costs involved, some brokers offer commission-free or low-cost options trading. It’s essential to research different brokers to find one that aligns with your trading preferences and budget. Additionally, be aware of any hidden fees or charges that may apply to your options trading activities.
Ready to dive into the exciting world of options trading? Join the GTF Options – Course today and unlock the secrets to successful trading.



 Facebook
Facebook  Instagram
Instagram  Youtube
Youtube 
