What Beta Coefficient Means for Investors?
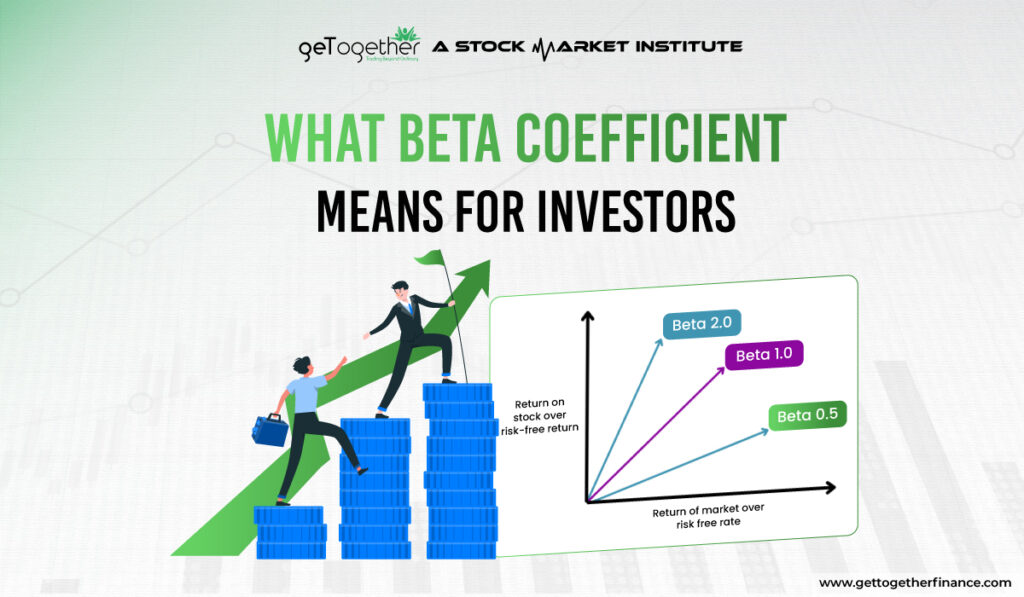
Beta Coefficient (β), currently you must be thinking about what this Greek word is doing in the world of the stock market. Well, let’s uncover the mystery behind beta, in the stock market, beta stands for volatility or risk that a stock or security as compared to the overall market.
For example, if NIFTY 50 currently has a beta of 1.0, then all the stocks that have a beta coefficient value higher than 1 will be at risk to trade compared to the NIFTY index. On the graph, beta represents the slope of the line through the regression of data points. Here, at each point, the stock or security’s returns compared to the market can be seen.
It is important to know how volatile or risky the stock is before investing in it. Are its highs too high or lows too low? Having the apt knowledge about this helps in analyzing the portfolio well, eventually knowing the risk that your portfolio will carry.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is the Beta Coefficient in the Stock Market and How Does It Work?

Simply, Beta (β) represents the volatility of the stock or security relative to the entire market. The fluctuations of the stocks compared to the indices and other market factors are studied in this coefficient. Knowing the beta coefficient of a stock is important in analyzing its risk.
The stocks with a higher beta are more volatile for example the stock has a beta of more than 1 i,e, 1.5, and the market rises 1 % than the stock can show a of 1.5% because its higher beta gives more volatility. So the beta helps you in analysing and assessing the risk in a security.
Beta coefficient is the major component of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM). This model helps in interpreting the expected returns of a stock based on its risk and risk-free rate.
Beta Coefficient Interpretation
The interpretation of beta in the stock market can be understood as:
- β=1, stock or security as volatile as the market
- β>1, stock or security is more volatile than the market
- β<1, stock or security is less volatile than the market
- β= negative, stock or security negatively correlated the market
This helps in interpreting that beta coefficients simply help in knowing how volatile the stock is compared to the current market scenario. Now, if the stock’s beta is greater than 1 (beta>1) then the stock is more volatile compared to the market.
Secondly, if the beta is less than 1 (beta>1) then the stock is less volatile compared to the market. If the beta is zero or negative then the stock can move in the opposite direction compared to the market.
Calculation of Beta Coefficient
One can use various spreadsheet programs embedded in Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets, which have built-in variance and covariance formulas, to calculate the beta coefficient for the stock or security. Here’s how it will work:
- Write data on weekly prices of the stock
- Write the weekly price of the market index you want to compare against (e.g, NIFTY 50)
- Calculate the weekly returns of the stock
- Calculate weekly returns of the index
- Use the slope function in the Excel program and select weekly returns of stocks and market as separate series
- The output from the slope is the Beta
Pros of Using Beta for Investors

Risk Assessment
A stock’s volatility compared to the market can be easily measured with beta. Stock being more volatile than the market index is considered riskier compared to the ones that fall under the apt scale. It also helps investors understand the systematic risk of the stock, which cannot be diversified away. This eventually helps investors in making informed investment decisions.
Portfolio Management
If an investor has stocks of different beta values, it helps them in creating a diversified portfolio. That keeps high beta (stocks with high volatility) stocks equal to low beta (stocks with low volatility), keeping the portfolio safe in uncertain market movements. This way, a combination of short-term as well as long-term gains goes hand in hand.
Also, investors can alter the overall risk of their portfolio by including stocks with different beta values to match their investment goals and risk tolerance.
Performance Prediction
The beta coefficient is a key component of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), it helps in knowing the expected return of a stock or security based on its beta value, the risk-free exposure, and the market return. Also, knowing a stock’s beta helps investors anticipate how the stock will perform in different market conditions, eventually helping in strategic planning and accurately timing the investment.
Benchmarking
Comparing the volatility and risk of the stock to the benchmark indexes of the market helps investors in knowing what they can expect from their investment decisions. Also, beta helps in comparing the risk to reward ratio that investors may get in the investment. Helping investors to assess whether they are getting good returns on the investment for the risk they are taking.
Cons of Using Beta for Investors

Historical Data Dependence
Since beta is calculated based on the previous movement of the stock and the index, it presumes that past volatility and market relationships will be transferred to future movements, which may not always be true. Completely relying on historical data can be misleading, especially if there are significant changes in the company’s operations or market conditions.
Ignores Company-Specific Factors
The beta coefficient only measures the market-related risks and oversees the company-specific risks, such as management changes, product recalls, or legal issues. If there are major changes in a company’s operations, strategy, or industry environment, it can heavily impact its risk profile, which beta might not be able to show with quantitative measures.
Market Dependency
Beta only relies on the market relation if the market conditions change drastically due to unforeseen circumstances like geo-political events, wars, or academics, then beta is no longer reliable. Further, the index chosen to compare the stock for calculating beta can influence its value. Different indices might yield different beta values for the same stock.
Volatility Misinterpretation
Beta will only give the volatility measure, but will not give a directional measure of the stock. A high beta indicates high volatility but does not specify whether the stock will go in an upward or downward direction.
Timeframe Sensitivity
The beta value can differ depending on the time period used for its calculation. If it is calculated over a short period it may differ significantly from beta calculated over a longer period.
This makes beta unstable over time, especially for stocks having irregular trading patterns
Simplistic Assumption
The beta coefficient is part of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), and it is a single-factor model. It only focuses on relevant risk, ignoring other factors of the stock like size, value, and momentum that heavily impact ROE for investors.
The linear graphical relationship represented between risk and return may not always be reliable as real-world stock markets are more complex and influenced by multiple factors.
Behavioral Factors
The behavior of investors or traders is not taken into consideration while calculating beta. It is a huge limitation, as the majority of the market is taken forward with the help of market sentiments only.
Conclusion
The beta coefficient is a crucial tool for investors, this is because it significantly helps in providing information about the volatility a stock has in comparison to the market. This significantly helps in risk management, portfolio diversification, and informed trading and investment decisions. It enables investors to predict the stock’s performance under different market conditions and evaluate the returns over time with risk.
However, it has disadvantages, such as relying on historical data, excluding company-specific risks, and being vulnerable to market changes and behavioral factors. Beta should not be the only indicator that investors use for making investment decisions. Instead, it should only be a part or add-on to the existing strategy. Knowing the pros and cons of the beta coefficient well allows investors to negotiate the complexities of the stock market and helps in making more informed investment decisions.
FAQs
What is the beta coefficient in the stock market?
The beta coefficient (β) assesses a stock’s volatility compared to the market. If the stock has a beta value of 1.0 then it shows that stocks are in line with market volatility. However, if the beta is higher than this, it indicates that the stock is more volatile than the market, whereas a lesser value than this indicates a low volatility compared to the market.
How does beta affect portfolio management?
Beta helps investors in building a diverse portfolio by balancing high-beta (riskier) stocks with low-beta (safer) stocks. This helps investors in managing overall risk and align the portfolio with their investing goals and risk tolerance.
What are the limitations of beta to make investment decisions?
The beta calculation is solely based on historical data, it ignores company-specific risks. It measures volatility but never specifies the stock is volatile in which direction and can be unstable over different time periods. Beta also does not consider the market sentiment or behavioral aspects that influence stock pricing.
How is the beta coefficient calculated?
To calculate beta, one needs historical price data for both the stock and the market index. Calculate weekly returns for both, then use spreadsheet software such as Excel to determine the slope of the regression line through the data points, which yields the beta value.
Can beta help predict future stock performance?
While beta gives the idea about a stock’s volatility and the risk it holds compared to the market, it does not predict future performance. Beta coefficient assumes that previous volatility patterns will always be there, which is not accurate due to changes in market conditions or company-specific factors.



 Instagram
Instagram
