What is the Difference Between Long-Term And Short-Term Trading ?

There are many different ways to trade in the financial markets, each designed to meet the needs and goals of different investors. Short-term and long-term trading are two common strategies used by investors. Investors trying to navigate the complicated trading world need to be aware of the differences between these approaches. We will examine the differences between long-term and short-term trading, as well as their characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations when selecting a trading style, in this blog.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding LONG-TERM trading:
Holding positions in the stock market for an extended period of time i.e. typically several months to years is known as long-term trading. Long-term traders aim to profit from an asset’s gradual increase in value by capturing its overall trend. This approach lines up with investors who focus on basic investigation, looking for resources with solid development potential and worth.
Investment decisions in long-term trading frequently are based on extensive research, fundamental analysis, and economic factors. Understanding that short-term volatility may not have a significant impact on the overall trajectory of their chosen assets, they typically have a higher risk tolerance.
Buy-and-hold investing, dividend investing, and value investing are some well-liked long-term trading strategies. In buy-and-hold investing, fundamentally sound assets are chosen and held for a significant amount of time to allow their value to rise.
Understanding SHORT-TERM trading:
In contrast to long-term trading, short-term trading involves buying and selling financial assets in a relatively short period of time, which can be as short as a single day or as long as a few weeks. Short-term traders intend to benefit from the unpredictability and cost changes happening inside these and they depend intensely on specialized research, technical analysis, and market trends to pursue their investment choices.
Short-term trading requires a more dynamic methodology, as dealers intently screen market developments and execute trades in light of daily price action. The objective is to profit from short-term market fluctuations, also known as scalping or day trading, by repeatedly making small profits.
Scalping, momentum trading, and swing trading are all common short-term trading strategies. Scalping involves making quick trades to take advantage of small price changes with the intention of making a profit from many transactions. Momentum trading centers around distinguishing resources with solid cost force, expecting to ride the pattern for momentary increases. Swing trading is the practice of profiting from upward and downward price movements by taking advantage of short-term price swings within a larger trend.
Key Distinctions between LONG-TERM and SHORT-TERM trading:
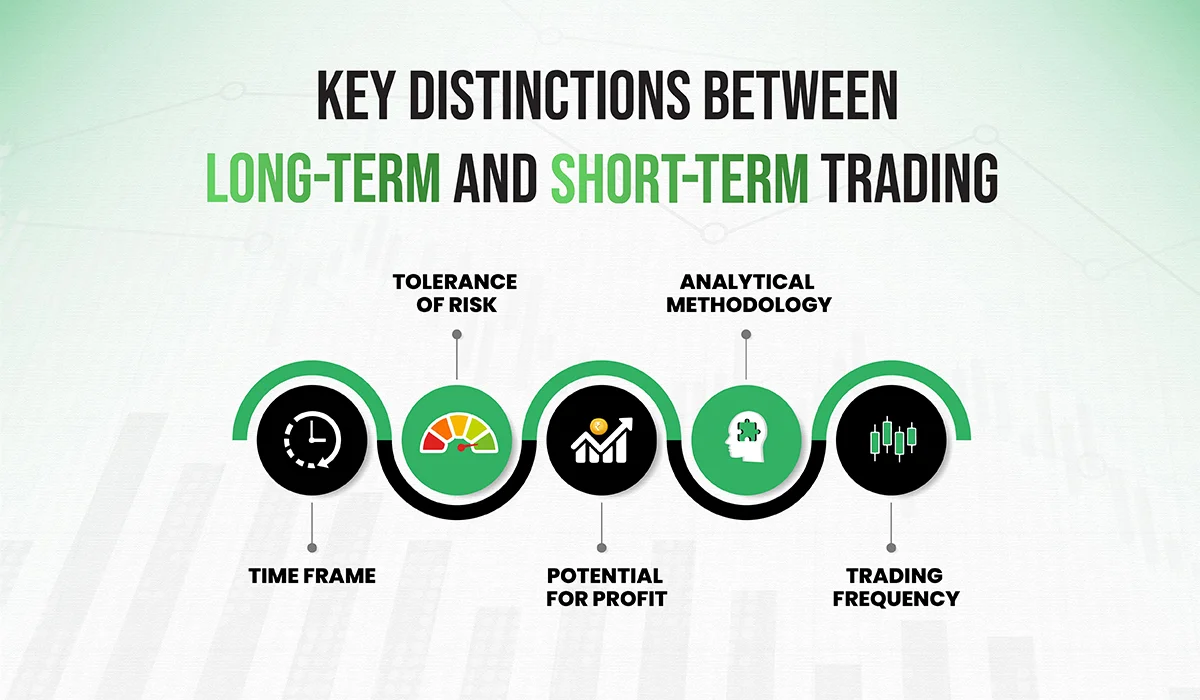
It is essential for traders to comprehend the key distinctions between long-term and short-term trading in order to select the strategy that best suits their financial objectives, risk tolerance, and trading preferences. Differentiating factors include:
Time-frame:
The essential qualification lies in the investment time span. Short-term trading involves much shorter holding periods, ranging from days to weeks, whereas long-term trading involves holding positions for months to years.
Tolerance of risks:
Long-term traders are those who are willing to endure short-term market fluctuations in the target of long-term growth, long-term traders typically have a lower risk tolerance. Short-term traders, on the other hand, use strategies that take advantage of short-term price movements to manage risk more actively.
Potential for profit:
The goal of long-term trading is to capture an asset’s overall growth and appreciation over a long period of time. While focusing on smaller price changes, short-term trading offers the potential for more frequent and immediate profits.
Analytical methodology:
Long-term trading heavily relies on fundamental analysis, economic indicators, and a thorough evaluation of a company’s prospects. Short-term trading places greater emphasis on technical analysis, price action, and market trends.
Trading frequency:
Since the emphasis is placed on maintaining positions for a longer period of time, long-term trading involves fewer transactions. Short-trading, conversely, requires more quick exchanging action, as dealers mean to catch numerous momentary benefits of opening doors.
Advantages of Long-Term Capital Gains

- Lower Tax Rates: Long-term capital gains are usually taxed at lower rates compared to short-term capital gains. Spending on the income level, some people’s gains do not fall under the tax-paying category.
- Tax Deferral: Compounding growth is encouraged when you keep your money invested for more than a year, by taking leverage of the gain that isn’t gone in taxes.
- Reduction of Investment Risk: Long-term holding periods can help you skip the uncertain market volatility and reduce the risk associated with market timing.
- Potential for Greater Returns: If we look at the bigger picture, long-term gains in reliable stocks have more return yield compared to short-term gains.
- Dividend Reinvestment: Long-term investment makes you eligible for dividends which can be reinvested too, increasing the value of your portfolio.
Also Read: https://www.gettogetherfinance.com/blog/income-through-dividend-investing/
Do Long-Term Capital Gains Rates Ever Change?
Yes, rates of long-term gains can change. Changes to these rates can occur due to:
- Legislative Changes: The elected government can pass new laws and monetary policies that alter the tax rates on long-term capital gains.
- Economic Policy Adjustments: Sudden changes in economic policies, often reflect shifts in governmental priorities, eventually resulting in changes in rates of long-term gains rate.
- Inflation Adjustments: Inflation may lead to changes in tax brackets of long-term gains which can impact the applicable tax rate for certain income levels.
Planning Long-Term & Short-Term Investment Strategies

- Long-Term Strategies:
- Buy and Hold: Investing in stocks or securities to hold them for several years, and enjoy the returns from compounding growth and potential capital appreciation.
- Retirement Accounts: Utilizing tax advantage accounts like NPS, tax saving investments PPF, etc.
- Dividend Growth Investing: Investing companies with significant dividend yield, getting rewarded for investment over time.
- Rupee-Cost Averaging: Investing a fixed amount of money regularly over time, irrespective of market conditions, to reduce the impact of market volatility and defer inflation.
- Short-Term Strategies:
- Day Trading: Buying and selling the stocks usually in a day to capitalize on short-term movements.
- Swing Trading: Holding the positions for more than a day to a week, to capitalize on ongoing short-term trends.
- Options Trading: Traders can use options contracts to speculate on short-term price movements or to hedge existing positions of equity or cash market.
- Market Timing: Traders use technical analysis to analyze the price movement of the stock and understand its stimulating points for getting entry and exit at the right points.
Who Might Consider Long-Term Investment Strategies?

- Retirement Savers: People whose aim is to save for retirement can benefit from the compounding growth that comes with long-term investing and also leverage tax advantages of long-term investments.
- Risk-Averse Investors: People who want to go with a stable and safe investment approach and wish to avoid the volatility associated with short-term market gains can do long-term investing.
- Busy Professionals: Investors who do not have much time to regularly monitor the ups and downs of stock should consider long-term investing.
- Growth-Oriented Investors: Investors who are seeking rewarding capital appreciation over time through investments in growth stocks
Who Might Consider Short-Term Investment Strategies?

- Active Traders: Traders who know technical analysis and want to enjoy potential short-term gains by actively monitoring the market can go with short-term investment.
- Speculators: Short-term investment is majorly for people who are looking to capitalize on short-term market movements and willing to take on higher risk.
- Professionals with Market Expertise: Only the ones with a deep and thorough understanding of the stock market technicalities and the ability to analyze short-term trends should go with short-term investments.
Income Seekers: investors or traders who need to generate quick regular income with the 0help of increased capital.
Factors to consider while choosing your trading style:
There are several factors to consider when choosing a trading style:
Financial goals:
Think about your financial targets and adjust them to the trading style that best suits your objectives. Long-term trading might be more appropriate for investors looking for value enhancement over the long term, while short-term trading might be interesting to those searching for frequent gains.
Risk tolerance:
Assess your risk tolerance and determine how comfortable you are with short-term market fluctuations. Long-term trading is generally less affected by short-term fluctuations, whereas short-term trading requires active risk management.
Time responsibility:
Find out how much time you can spare for trading. Long-term trading calls for less time responsibility, including fewer trades and less tracking. More active participation and constant market observation are required for short-term trading.
Economic situations:
Take into account the current market conditions and volatility. Long-term trading can be stronger to financial market variances, while short-term trading depends on good economic situations with higher instability and cost developments.
Conclusion
The distinction between long-term trading and short-term trading lies essentially in the time period of investment, risk appetite, benefit potential, logical methodology, and trading frequency. There are advantages and disadvantages to both types of trading, and which one is best for you will depend on your financial objectives, tolerance for risk, commitment to time, and market conditions.
By figuring out the variations between long-term and short-term trading and taking into account the elements talked about, investors can pursue informed choices that can improve their trading experience and improve the probability of completing their financial targets.
CATEGORIES



 Facebook
Facebook Instagram
Instagram Youtube
Youtube
