What is Return on Equity (ROE)?
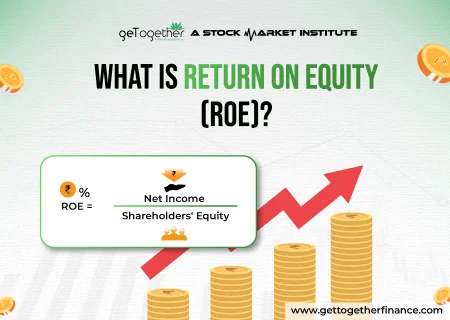
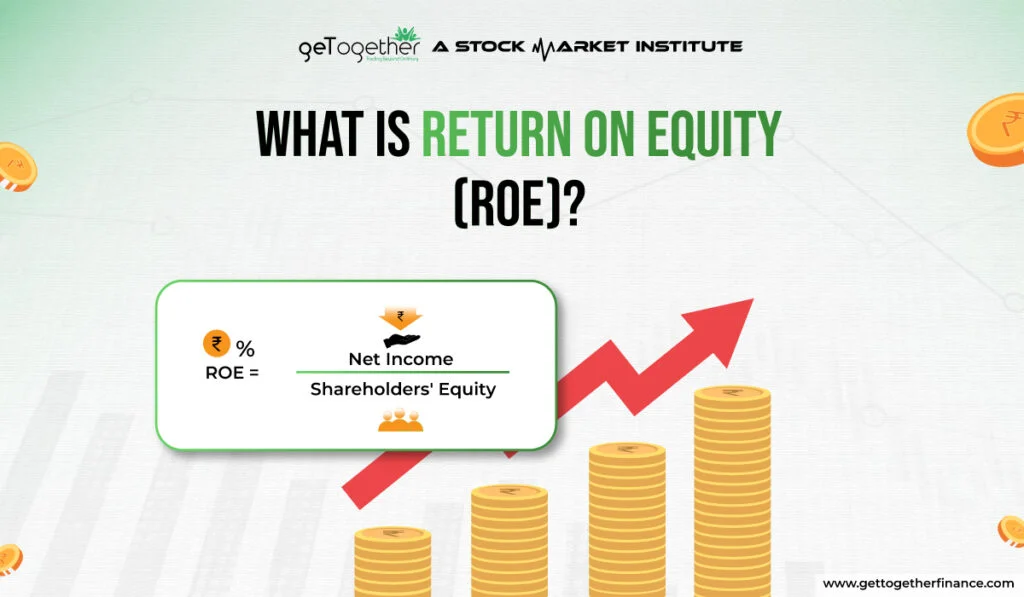
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview
Ever come across the term “ROE” in the financial world and wondered what it meant? You’re not alone. Return on Equity (ROE) is a financial ratio that can be a bit confusing at first glance.
The Return on Equity (ROE) is a powerful metric that dives deep into this very concept. It goes beyond simply looking at profits and instead reveals how efficiently a company is using its shareholders’ money to generate those profits.
This blog will explore what is ROE, how it works, and how to calculate the return on equity on your investment. Let’s begin the drill without any delay.
What is Return on Equity (ROE)?
Return on Equity (ROE) shows how much profit a company makes with each dollar of equity from shareholders. Expressed as a percentage, ROE is useful for assessing how well management uses shareholders’ funds to generate profits and grow the company.
In simpler terms, think of it as a profitability report card. It tells you how much profit a company generates for each buck of shareholders’ equity. It’s a measure of a company’s efficiency in using shareholder money to create returns. It helps investors make informed decisions. A high ROE generally indicates a company is effectively using shareholder capital, while a low ROE might suggest areas for improvement.
Also Read: Solvency Ratio
Return on Equity Formula (ROE)

Now that we understand the significance of Return on Equity (ROE), let’s equip ourselves with the formula to calculate it. Here’s the magic equation:
ROE = Net Income / Shareholders’ Equity
Where;
- Net Income: This represents the company’s profit after all expenses have been accounted for. It’s essentially the “bottom line” on the income statement.
- Shareholders’ Equity: Think of this as the company’s net worth, calculated by subtracting total liabilities from total assets. It represents the money invested by shareholders.
If a company sells all its assets to pay off its debts, whatever is left is the shareholders’ equity. You can find this equity directly on the balance sheet or by subtracting liabilities from assets.
Shareholders’ equity is a book value, not the market value (market capitalization). Since it’s the company’s total assets minus its total liabilities, ROE is sometimes called “return on net assets.” Average net income is used because the income statement covers a period, while the balance sheet shows a specific point in time.
Also Read: EBITDA Margin
What Return on Equity Tells You

Whether an ROE (Return on Equity) is good or bad depends on the industry standards. For instance, utility companies, with lots of assets and debt but lower net income, might have a typical ROE of 10% or less. Conversely, tech or retail companies, with higher net income relative to their balance sheet, might have an ROE of 18% or more.
Generally, aim for an ROE at or slightly above the sector average. For example, if a tech company, TechCo, has a consistent ROE of 18% while its peers average 15%, TechCo is performing well in using its assets to generate profit.
High or low ROE varies across industries. A quick check for investors is to see if the ROE is close to the long-term average of around 13% for the Nifty 50. Anything below 10% is usually considered poor.
Benefits & Limitations of ROI (Return on Equity)?

Return on Investment (ROI) is a widely used metric in finance to assess the profitability or efficiency of an investment. It essentially measures the net gain or loss compared to the initial investment. While ROI provides valuable insights, it’s important to understand both its benefits and limitations.
Benefits of ROI
- Simplicity: ROI is a straightforward calculation, making it easy to understand and interpret, even for non-financial professionals.
- Performance Benchmark: ROI allows you to compare the performance of different investments across various asset classes, providing a common ground for evaluation.
- Decision-Making Tool: By calculating ROI, you can assess the effectiveness of past investments and make informed decisions about future investments.
- Risk-Return Relationship: ROI helps you understand the relationship between risk and return. Generally, higher potential returns are associated with higher risks.
Limitations of ROI
- Time Horizon Blindness: ROI doesn’t consider the time value of money. An investment that takes longer to generate returns might appear less attractive compared to a quicker option, even if the overall gain is higher.
- Ignores Cash Flow: ROI focuses solely on the net gain or loss, neglecting the timing of cash flows. An investment with consistent cash flow throughout the investment period might be undervalued by ROI compared to an option with a lump sum return at the end.
- Limited Qualitative Factors: ROI is a purely quantitative measure. It doesn’t take into account qualitative factors like the impact of inflation, market volatility, or the strategic value of the investment.
- Industry Specificity: Comparing ROI across different industries can be misleading. Certain industries have inherently higher or lower ROI ranges due to their business models or risk profiles.
| Benefit | Description | Limitation | Description |
| Simplicity | Easy to calculate and understand | Time Horizon Blindness | Doesn’t consider time value of money |
| Performance Benchmark | Compares performance across investments | Ignores Cash Flow | Neglects the timing of cash flows |
| Decision-Making Tool | Informs future investment decisions | Limited Qualitative Factors | Ignores qualitative factors like inflation |
| Risk-Return Relationship | Shows risk vs. return relationship | Industry Specificity | Can be misleading across industries |
High ROE Stocks in India

Here are few high return on equity stocks in India that you need to know:
| Sector | Company | Current Price (₹) | Market Cap (Cr) | ROE (%) |
| Information Technology | Infosys | 1,825.40 | 6,24,378.23 | 28.42 |
| Consumer Goods | Hindustan Unilever | 4,287.10 | 5,84,129.47 | 23.15 |
| Pharmaceuticals | Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories | 4,932.50 | 1,02,347.12 | 21.78 |
| Automobiles (2 & 3 Wheelers) | Bajaj Auto | 4,125.20 | 1,34,756.80 | 20.98 |
| Banking & Finance (Private) | HDFC Bank | 2,542.10 | 8,34,721.38 | 18.37 |
In A Nutshell
In essence, exploring Return on Equity (ROE) equips you with a valuable tool to assess a company’s profitability and efficiency in using shareholder investment. While a high ROE generally indicates strong financial health, it’s crucial to consider industry benchmarks, historical trends, and combine ROE with other financial metrics for a complete picture. Remember, ROE is just one piece of the puzzle. By understanding its strengths and limitations, you can make informed investment decisions and unlock the potential for sustainable returns.
FAQs
How will ROE be relevant in the future of investing?
As financial analysis continues to evolve, the interpretation and application of ROE might adapt. However, ROE is likely to remain a valuable tool for investors seeking to understand a company’s profitability and efficiency in using shareholder capital.
What are some alternatives to ROE?
Other profitability ratios like Return on Assets (ROA) or profit margin can provide additional insights.
Does ROE affect a company’s stock price?
Investors often consider ROE when valuing a company, so a high ROE might contribute to a higher stock price. However, it’s not the sole determinant.
Is there a “perfect” ROE for investment?
No, there’s no magic ROE number. A "good" ROE depends on the industry, company size, and your investment goals. Diversification is key. While a high ROE is a positive indicator, consider factors like growth potential, valuation, and overall financial health.



 Facebook
Facebook Instagram
Instagram Youtube
Youtube
